The side effects of ARBs
#Side Effects of ARBs (Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers)#

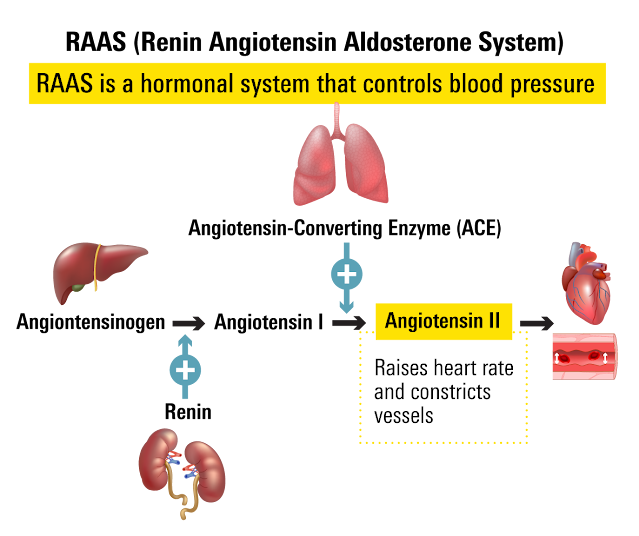
By inhibiting this effect, ARBs help relax blood vessels, lower blood pressure, and improve overall heart function. While generally well-tolerated, ARBs can cause a variety of side effects, some mild and others more serious. In this article, we'll learn about the common and less common side effects of ARBs, how they work in the body, and how to manage potential adverse effects.
Common Side Effects**
A. Dizziness and lightheadedness**
One of the most common side effects of ARBs is dizziness, especially when standing up suddenly. This occurs because ARBs lower blood pressure, which can result in a temporary drop in blood flow to the brain when a person changes posture.
B. Hyperkalemia (increased potassium levels)**
Potassium is an essential mineral that helps maintain normal cell function, especially in the muscles and heart. However, excessive potassium can lead to serious complications, including irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias). Regular blood tests to monitor potassium levels are usually recommended for patients on ARBs.C. Fatigue**
Fatigue or exhaustion is another frequently mentioned side effect. As the body adjusts to the low blood pressure induced by ARBs, some individuals may experience weakness or lack of energy. Although this is not usually a major concern, patients who feel persistently tired should consult their healthcare provider to rule out other possible causes.
D. Low Blood Pressure (Hypotension)**
Since ARBs lower blood pressure, some patients may experience hypotension, especially when they begin treatment or if their dose is increased. Symptoms of low blood pressure include dizziness, fainting, and feeling weak. This effect is usually more pronounced in patients who are already taking other antihypertensive medications, are elderly, or have a history of low blood pressure.
A. Angioedema**
This swelling can obstruct the airway, causing difficulty breathing and potentially fatal respiratory distress. Angioedema is a known risk of both ARBs and ACE inhibitors (another class of blood pressure medications). If a patient experiences swelling of the face, mouth, or throat, they should seek emergency medical help immediately.B. Kidney Dysfunction**
ARBs can affect kidney function, especially in individuals who already have kidney disease or who are at high risk. The kidneys depend on a specific balance of hormones and blood pressure to function properly. By altering the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), ARBs can reduce the kidney's ability to filter waste products, leading to increased levels of creatinine, a marker of kidney function. Severe kidney impairment may occur, especially in patients with diabetes, heart failure, or other chronic conditions. Regular monitoring of kidney function is recommended during ARB therapy.
C. Liver Problems**
In rare cases, ARBs can cause liver dysfunction. This may manifest as elevated liver enzymes in blood tests or symptoms such as jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes), dark urine, and abdominal pain. If these symptoms occur, the patient should stop taking the medication and contact their healthcare provider immediately for evaluation and possible alternative treatment.
D. Pregnancy Risks**
They can cause serious birth defects, kidney damage, and fetal death. Women who are pregnant or planning to become pregnant should inform their healthcare provider before starting ARBs.
#Other Possible Side Effects#.jpg)
.jpg)
A. Cough**
Although less common than with ACE inhibitors, some individuals may experience a dry, persistent cough while taking ARBs. This side effect is due to the way ARBs affect the RAAS system, although it generally occurs less frequently and is less severe than with ACE inhibitors.
B. Gastrointestinal Problems**
Some individuals may experience a dry, persistent cough while taking ARBs.
Click here more site>>>>>>>>>Enjoy in gurugram
.jpg)


Comments
Post a Comment