Muscle Repair More Active During REM Sleep Or Non-REM Sleep Stages
Sleep is an essential biological process that plays a key role in recovery, memory consolidation, and tissue repair. One of its most important functions is to assist the body in repairing muscle and other tissues after physical activity or injury. The question of whether muscle repair is more active during stages of rapid eye movement (REM) sleep or non-REM sleep is complex but highly relevant to understanding how the body heals and regenerates. Current scientific evidence strongly suggests that muscle repair is more active during non-REM (NREM) sleep, particularly the deeper stages, not during REM sleep. This essay explores the different sleep stages, their physiological functions, and their relation to muscle repair processes. A typical night of sleep moves through these stages in approximately 90-minute intervals, with each complete cycle consisting of both NREM and REM stages.In contrast, REM sleep is characterized by high brain activity, rapid eye movements, vivid dreams, and temporary muscle paralysis (atonia), except for the essential muscles that control breathing and eye movement.
#Hormonal Activity and Muscle Repair#
Muscle repair and growth are primarily controlled by hormonal activity, particularly the release of growth hormone (GH). Research suggests that most growth hormone secretion occurs during deep NREM sleep, particularly in stage N3. This suggests that the body's capacity for muscle repair is at its peak during this stage.During slow-wave sleep, there is an increase in parasympathetic nervous system activity, which promotes a relaxed state conducive to anabolic processes such as tissue growth and repair.In contrast, REM sleep is more associated with neural activity, memory consolidation, and emotional processing rather than physical repair.Additionally, during NREM sleep, particularly in stage N3, blood flow is directed away from the brain and toward the muscles, allowing oxygen and nutrients to reach damaged tissues more effectively. This blood flow shift supports the delivery of amino acids and other essential components for muscle regeneration.
#The Role of REM Sleep in Recovery#
REM sleep plays an important role in mental recovery, emotional regulation, and restoration of the central nervous system. Since muscle function is intricately linked to the nervous system, REM sleep indirectly supports muscle health by maintaining the efficiency of motor neurons and neuromuscular communication. However, these effects are more about optimizing coordination and less about actual tissue repair.In addition, REM sleep affects the consolidation of motor skills learned during the day. Athletes and physically active individuals can benefit from REM sleep in terms of strengthening muscle memory and recovering movements. Although this is not the same as repairing torn muscle fibers, it is still an important aspect of recovery for performance enhancement.
#Scientific Studies and Evidence#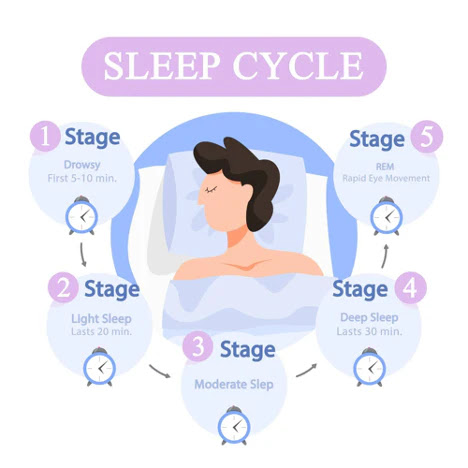
Several studies conclude that muscle repair is most active during NREM sleep. An important piece of evidence comes from sleep deprivation experiments. When subjects are deprived of slow-wave sleep, their growth hormone levels are significantly reduced, and their recovery from physical exertion is impaired. In contrast, when individuals experience more slow-wave sleep, their physical recovery appears to be faster and more complete.In addition, studies involving athletes show that increased deep sleep is related to improved recovery markers, such as reduced muscle soreness, lower levels of inflammation, and improved performance in subsequent training sessions. Understanding that muscle repair is more active during NREM sleep, particularly in the deep sleep stages, is important for health, fitness.
Click here more site>>>>>>>>>Enjoy in gurugram

.jpg)


Comments
Post a Comment